Find the best antennas for TV, radio, and wireless. Compare top antenna deals, use free antenna calculators, follow DIY guides, and buy high-performance antennas with confidence.
Buil This High Gain Rhombic TV Antenna
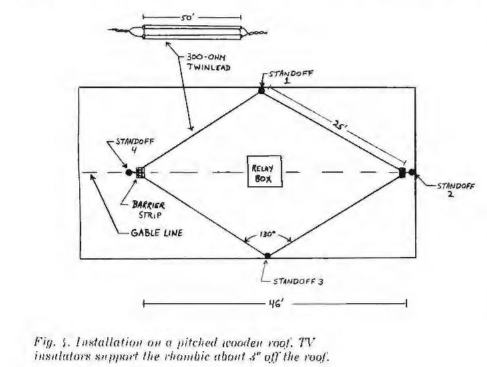
This Rhombic Antenna was from Popular Electronics Magazine October 1975 Edition. Cheap cost Antenna , and if your roof house non metallic can match with contour house. Easy to build and Install , provides good reception , almost 14 dB gain. It can be installed without support masts. High gain, broad bandwidth and good directionallity are characteristic of the rhombic's performance.
Rhombic Antenna Design
The first step in designing the rhombic is to decide what channels you want to recieve.
The relative location of their transmitting antennas with respect to your home. And the physical layout of the installation site ( we assume the antenna is mounted horizontally on the pitched roof of wood house) , for modern today house we should move antenna to outside of roof, because today house construction using steel frame.
For optimum result three basic designs are given, covering VHF Lo, VHF Hi, and UHF Bands. The VHF Lo Antenna measures 25 Feet ( 7.6 m) on a side and cover channels 2 through 6 and the FM Broadcast Bands.
The VHF Hi design , spanning channels 7 through 13, has legs one-third the length of those for VHF Lo.
Our TV Antenna Type and Specification List we can offer
TV Antenna
Type : YNX-HD-T-C01
Specification
TV Antenna
Type : YNX-HD-T-C02
Type TV Antenna
YNX-HD-T-C03
Type TV Antenna
YNX-HD-T-C04
Specification
Minimal Quote : 100 pcs , maximum Quote : 5000 pcs
Build The Microcomputer SAP-1 (Continues 1)
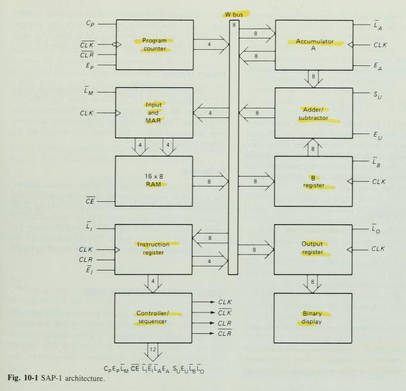
As described in article before about the architecture of Microcomputer SAP-1 , in this article we will continue with other part of Microcomputer Diagram Block and circuit .
For you reference , in figure 10-1 as described have Instruction Register, Accumulator, B Register, Output Register, and Binary Display, We will describe all about it in this article.
For you reference , in figure 10-1 as described have Instruction Register, Accumulator, B Register, Output Register, and Binary Display, We will describe all about it in this article.
Instruction Register
The Instruction register is part of the control unit. to fetch an instruction from the memory the computer does a memory read operation.
This places the contents of the addressed memory location on the W bus . At the same time, the instruction register is set up for loading on the next positive clock edge.
The contents of the instruction register are split into two nibbles. The upper nibble is a two-state output that goes directly to the block labeled "Controller sequencer". The lowe nibble is a three-state output that is read onto the W bus when needed.
Controller-Sequencer
The lower left block contains the controller-sequencer. Before each computer run, a Low CLR signal is sent to the program counter and a CLR signal to the instruction register.
Kivy Example Program "Hello World"
class TestApp(App):
def build(self):
return Button(text='Hello World')
TestApp().run()
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)