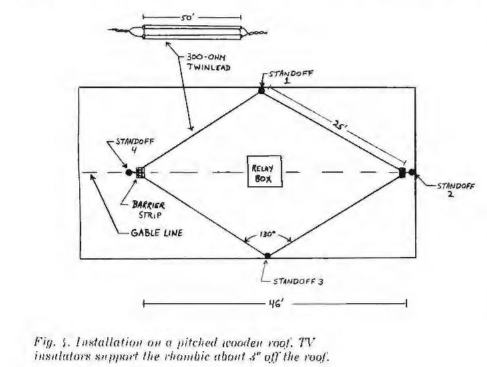
With todays many cellular tower in the rural areas, and affect TV signal reception , we also need cellular filter 3G/4G/5G.
For this purpose I will compare GE Outdoor TV Antenna VS Antennas Direct Outdoor Antenna with keys criteria for you as reference.
If you live in USA and Canada please check your coverage in FCC website.
Check Coverage
Use dtv reception maps to check for the DTV signals that are available at your location. Enter your address in the box at dtv reception maps and click Go! The DTV coverage map will list all stations in your area.
Sometimes stations change the frequency on which they broadcast — the channel a viewer selects to watch a particular station remains the same but the frequency that the viewer’s television finds the station on changes -- requiring viewers who use an over-the-air antenna to rescan their tuners to locate the station's new signal.
DTVmaps is a tools to help you decided what the right antenna for your TV, based on coverage distance.
Actual signal strength may vary based on a variety of factors, including, but not limited to, building construction, neighboring buildings and trees, weather, and specific reception hardware. Your signal strength may be significantly lower in extremely hilly areas.
Comparison chart
Below the chart comparison is a key to explain each of the measurements and what to compare depending on your needs.
The keys factor you need to know for pick the Antenna Outdoor are :
Brand
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate incorporated in New York State and headquartered in Boston. As recently as 2018, the company operated through the following segments: aviation, power, renewable energy, digital industry, additive manufacturing, locomotives, and venture capital and finance . One of GE products are home appliances included TV Antenna.
Antennas Direct is An Antenna company in 16388 Westwoods Business Park Ellisville, MO 63021, whose acquired Mohu Antenna in 2003, have more than 100 employees, and produce Innovative HDTV Antennas, Broadcast Television, Digital Antennas, TV Antennas, OTA Television, Television Accessories
Different manufactures produce Outdoor Antenna which meet today’s good reception standards antenna. The chart shows the criteria for you considered to picks the antenna
Model
The 2 Antenna model name shown are different, GE model with J mount and designed for reduce signal dropouts and for UHF, VHF, HDTV reception, claims by customer to have power reception around 16-20 dB can installed both Outdoor, Attic and Indoor .
While Antenna Direct model with 8 element bowtie, also can installed in Outdoor, Attic, and Indoor and have around 17.4 dB power reception, it is strong enough to receive long distance broadcast TV Tower.
Filter
Lte filter can remove interference from frequency bands (3G/4G) outside the TV band. It can improve the TV signal.
Passes range 80 to 800MHz,Blocked 800MHz above.4g filter removes noise for better picture. Antenna Filter - Cleaning unwanted RF signal out of digital antenna system effectively,Signal loss is 0.8dB or less.
Booster
Signal booster enhances any non-amplified antenna, delivering a clearer signal, more range, and more available channels; works with any passive/non-amplified antenna; antenna required for use with preamplifier.
This questions must apply before you buy the booster :
Are your home/house far away from TV Tower Stations and also have weak signal reception from Outdoor/Indoor Antenna ? If the Answers is Yes, than you should use Booster Antenna.
Range Max (in Miles)
Range Antenna for pick up TV signal influenced by Elements of Antenna and Gain , the more elements your antenna have, the more Gain of the Antenna, and more sensitive to pick signal from far away
Gain (in dBi)
As mention above, the more Gain the antenna have, the more good quality for antenna pick up signal.
If the antenna have Gain between 15-35db , it is good enough for receiving TV signal from long range area.
Band (Frequency in MHz)
Band frequency for Digital HDTV, VHF, and UHF band between 470-860 MHz , sometimes antenna manufacturing company also made antenna covering FM Band, between 45-860 MHz.
Price
Price will vary, you can get the cheapest antenna with price below USD 30 , or the expensive one with price more than USD 200, it is depends your need, as long as you have the good quality of antenna, with the good reception and your satisfied , the price will not be the issue.